Introduction
Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) are often seen as a hallmark of success and a major milestone for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). SMEs often embark on the journey of becoming publicly listed companies with great optimism, envisioning increased capital, enhanced credibility, and accelerated growth. However, the reality post-listing can be fraught with challenges. However, while an IPO can provide a company with the necessary capital to expand and grow, many SMEs struggle to sustain themselves in the post-IPO period. In order to understand this better it is necessary to analyse performance of SMEs.
Data for Analysis
We randomly selected ten sectors and one listed SME company from each sector for analysis. We analysed the growth in the revenue and net profit of the companies before and after listing of the company which sheds light on some of the reasons behind this phenomenon. In this article we shall deliberate on probable reasons for why SMEs struggle to sustain after listing.
For future sustenance of company, understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for the sustainability of SMEs in the public market.
Upon examining the financials of randomly selected listed SMEs before and after their listing, it has been observed that many SMEs struggle to achieve steady growth even after securing funds from the public (ref. Image 1& 2 Below, Source of Data: Taken from Annual reports of the selected sample companies.).
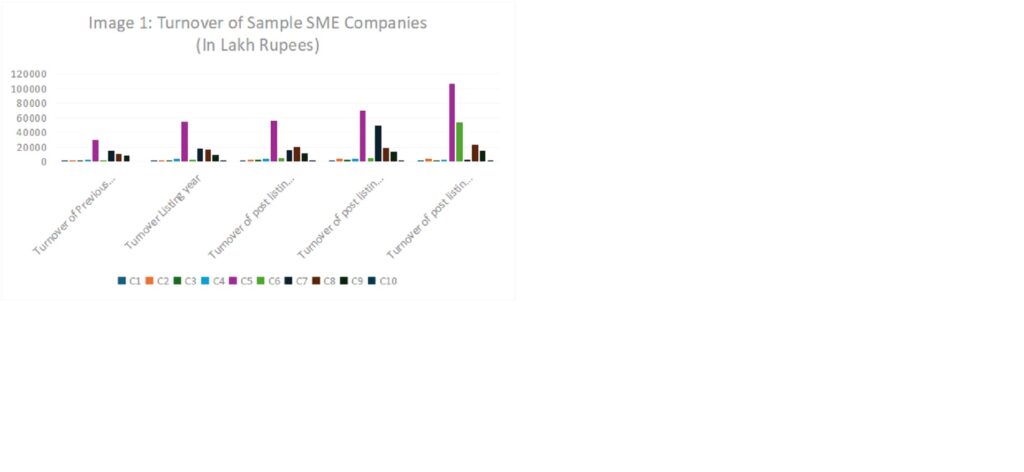
Image 1: Change in Turnover of Randomly selected companies from the financial year before listing, the listing year and that of years after listing.
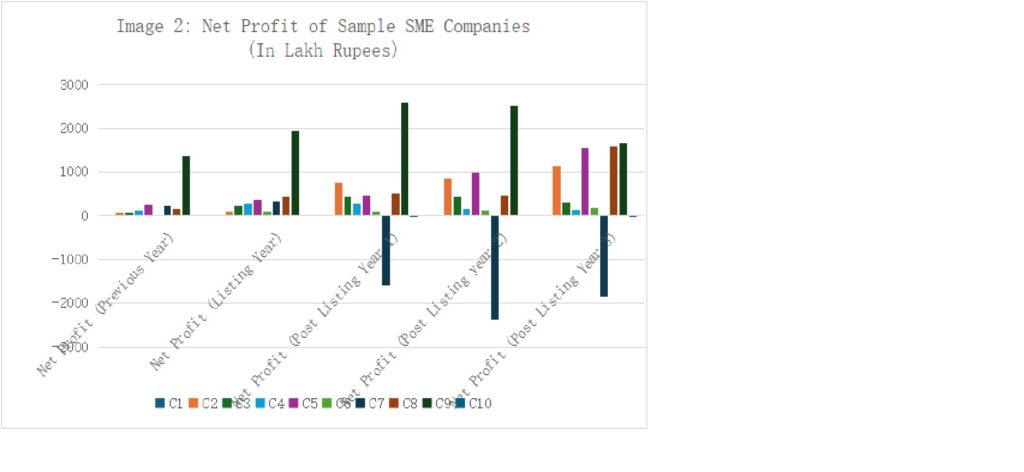
Image2 : Change in net Profit of Randomly selected companies from the financial year before listing, the listing year and that of years after listing.
Based on the graphs above, it is evident that SMEs typically list on stock exchanges to raise capital intended for the company’s growth, which ideally should be exponential. However, the data reveals a different trend. While some companies have shown consistent growth, only a few have achieved exponential expansion. The majority of these companies struggle to reach this level, with some even experiencing losses.
The potential reasons or root causes for these outcomes are as follows:
- Access to Capital:
When SMEs decide to list on a stock exchange, they aim to enhance their access to capital. However, they often face the challenge of not receiving the expected investment influx. Investors typically perceive SMEs as riskier compared to larger, well-established companies. Therefore, engaging with potential investors consistently becomes crucial for SMEs. It can be achieved by presenting a clear and compelling story about the company’s growth potential and financial stability.
- Operational Inefficiencies:
SMEs often lack the sophisticated operational setups of larger companies. When they go public on a stock exchange, they come under pressure to scale up, which can expose these inefficiencies. To tackle this issue effectively, SMEs need to focus on streamlining their processes, investing in technology, and strengthening their operational oversight. These steps are vital for them to successfully adjust and thrive after listing.
- Market Competition: Battling the Giants
After SMEs list on a stock exchange, they often face a daunting competitive landscape where larger companies dominate with greater resources and market presence. To navigate this challenge successfully, SMEs must emphasize their unique strengths and leverage them to carve out a stable and enduring position in the market. This strategic focus is essential for them to thrive amidst larger competitors.
- Management Expertise:
When SMEs transition to becoming publicly listed companies, they face a significant demand for heightened management expertise. This shift can be challenging because their leadership teams may lack prior experience dealing with the complexities of public company governance. As a result, many SMEs find this transition period quite daunting. It underscores the importance of acquiring the necessary skills and support to effectively manage the responsibilities that come with being a publicly traded entity.
- Market Volatility: Weathering Economic Storms
SMEs often find themselves at greater risk during times of market volatility and economic downturns. This vulnerability stems from the fact that fluctuations in market conditions can exert a more significant impact on their financial stability compared to larger, more established companies. It underscores the importance for SMEs to be prepared to navigate these challenges with resilience and strategic planning to safeguard their operations and sustainability in uncertain economic environments.
- Investor Relations:
For SMEs, maintaining effective investor relations is crucial to sustaining investor confidence. However, SMEs often face challenges in this area because they may lack dedicated resources or expertise for investor relations. As a result, managing communication and engagement with investors can be particularly demanding. It highlights the importance for SMEs to prioritize building strong relationships with investors, communicating their company’s performance and growth prospects clearly and consistently, despite resource limitations. This proactive approach can help SMEs enhance transparency and trust, essential for long-term investor support.
- Economic Conditions:
SMEs are often more sensitive to broader economic conditions, such as inflation, trade policies, and geopolitical events. These factors can have a significant impact on SMEs, potentially affecting their operations and financial stability to a greater extent than larger corporations. Therefore, SMEs need to stay vigilant and adapt quickly to changing economic landscapes. This adaptability is crucial for them to navigate challenges effectively and sustain their growth amid external economic pressures.
Conclusion:
Becoming publicly listed through an IPO is a significant milestone for SMEs, promising increased capital and credibility. However, the reality often includes challenges that can hinder sustained growth post-listing. Issues such as limited access to capital, operational inefficiencies, intense market competition, and the need for enhanced management expertise and investor relations all contribute to these difficulties. Moreover, SMEs are more vulnerable to market volatility and economic downturns, further complicating their path to stability. Addressing the challenges of declining performance post-listing for SME companies can be achieved through the following initiatives:
- Strategic Focus: Prioritizing long-term goals and aligning business activities to enhance growth and market positioning.
- Proactive Management: Anticipating market changes and making timely decisions to mitigate risks and seize opportunities.
- Adaptability: Embracing flexibility and innovation to respond to evolving market dynamics and ensure sustained success in the public market.

